


The power supply refers to the power source of the forklift, which can include an engine or batteries depending on the type of forklift. For electric lift trucks, the battery acts as a counterweight. Internal combustion forklift counterweights are located toward the back of the forklift, or on the opposite side of the forks. Check the rating plate on the forklift for this information. Forklifts are designed with maximum carrying capacities using the counterweight for balance, so it is important to know the carrying capacity intended for the forklift. This helps keep the forklift stable during lifting and traveling operations. The counterweight is the weight installed onto the forklift to help offset the weight being lifted by the forklift. It is also important to never remove the backrest before operating the forklift for your own safety as well as the well-being of the forklift. It is important to use a load backrest that is designed for the forklift. The forklift backrest also helps protect the forklift mast and mast components from being damaged by the load. This helps prevent the load from slipping backwards toward the forklift operator during lifting and travel conditions. The forklift backrest provides the operator another surface to rest the load against and is attached to the carriage. Standard ITA forks are the most common type of forklift forks, but they too come in various widths, lengths and shapes. There is a wide variety of fork types available for various applications. Forklift forks come in all shapes and sizes. They are attached to the forklift carriage and are designed to carry a load from the bottom. The forks on a forklift are used to make direct contact with a load for transport. Perhaps the most obvious of reach truck parts are the forks themselves, also known as the tynes. This includes the forks of the forklift, the load backrest and other features of a forklift truck that come in direct contact with the loads. The carriage is a platform located in front of the forklift mast that is used to mount objects to be controlled by the mast. The key difference is that the tilt cylinder controls the tilt movement of the carriage and the angle of the forks relative to the ground. Similar to the lift cylinder, the tilt cylinder controls movement for operation purposes. The lift cylinder is generally hydraulically powered and is a single-acting hydraulic cylinder, meaning it pushes in one direction. The forklift lift cylinder powers the vertical movement of the mast, or the raising or lowering of the forklift carriage and the forks.

This will allow you to select a forklift that is designed to fulfill the specific needs of your applications.įor more information on forklift masts, read our article Forklift Mast Types.
#KOMATSU FORKLIFT PARTS DIAGRAM FREE#
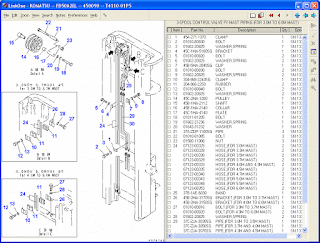
When selecting a forklift, it is important to familiarize yourself with the different features and terminology of a forklift mast: the mast’s lift height, the free lift height and the extended height and the lowered height. For most forklifts, the mast is designed toward the front of a forklift and directly in the forklift operator’s line of vision.įorklift masts come with various sections that elevate or lower the forklift carriage along with the forks. The forklift mast is the raised vertical support that allows loads to be raised and lowered. Understanding the terminology of the parts and anatomy of a forklift is important for effective communication with others while on the job. Here are some of the fundamental features and parts that make up the anatomy of a forklift truck. Forklifts have many moving parts and pieces that allow the forklift to operate properly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
